How Does a Welding Machine Work – Step by Step Process
Introduction
Welding is at the heart of modern manufacturing, from jewellery and medical devices to industrial mould repair and heavy engineering. At Asian Laser, with over 30 years of experience in laser technology, we have built deep expertise in providing laser welding machines that deliver precision, depth, and repeatability.
In this blog, we explore how a welding machine works, covering both electric welding and laser welding, step by step. We’ll also highlight the principles, types of welding (1G–6G), safety procedures, and the specific advantages of laser welding, especially as offered by Asian Laser.
What Is a Welding Machine? Definition & Uses
A welding machine is a device that joins two or more pieces of material, typically metals by applying heat, pressure, or both. Traditional welding uses electric arcs, while laser welding uses a concentrated beam of light. Asian Laser, for instance, offers a variety of laser welding machines, from portable pen welders to heavy-duty industrial welders.
Uses of welding machines include:
- Jewellery repair (micro-welding)
- Mold repairing in industrial tooling
- Automotive, solar, electronics, hardware, and dentistry applications
- 3D alphabet / signage welding
How Does Welding Work Step by Step?
Here is a step-by-step overview of how a welding machine works, covering the general principle and then diving into electric vs. laser welding.
Preparation and Setup
- Select the right welding machine for your application. For example, Asian Laser offers fibre pen welders (ALF 1000 / 1500) or desktop welders (ALDT 120) depending on precision needs.
- Clean and align the workpieces to ensure good contact.
- Configure the machine parameters: power, pulse frequency, duty cycle (for lasers), or current, voltage, and polarity (for electric).
Power Generation
- In electric welding, power comes from a welding power source (AC or DC), producing an electric arc between an electrode and the workpiece.
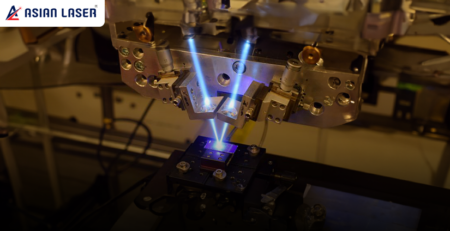
- In laser welding, a high-intensity concentrated beam (from a fibre laser) is generated. For example, Asian Laser’s Fiber Laser Pen Welding machines concentrate energy in a tiny spot for precise, deep welds.
Energy Delivery to the Workpiece
- For electric welding, the arc melts the base metal and (optionally) filler material, creating a molten weld pool.
- For laser welding, the focused laser beam heats a localized region very rapidly, creating a deep, narrow molten pool with minimal heat-affected zone (HAZ). Asian Laser’s machines are designed to minimize deformation, thanks to their controlled heat input.
Weld Pool Formation & Control
- The molten pool is maintained by controlling parameters (current, voltage, speed, pulse). In lasers, one controls peak power, pulse repetition rate, and pulse width. Asian Laser’s ALDC 200, for example, uses precise pulse control to manage energy deposition.
- The operator often moves the welding head (or workpiece) to traverse the joint.
Solidification
- Once the heat source moves on, the molten pool cools and solidifies, forming a strong metallurgical bond.
- The cooling rate, which depends on the energy input, can affect microstructure, residual stress, and distortion.
Post-Weld Processes
- Inspection: Check for defects like cracks, porosity, or incomplete fusion.
- Cleaning: Remove any slag (in electric welding) or spatter. For laser welds, cleaning may not be needed due to precision.
- Post-treatment: Heat treatment, polishing, or passivation may be used depending on application.
Principle of Electric Welding Machine
The working principle of an electric welding machine relies on establishing an electric arc (or resistance heating) between a consumable or non-consumable electrode and the workpiece. The arc’s heat melts the metal. Variations include MIG, TIG, stick, and resistance welding. Key control parameters are current, voltage, polarity, and shielding gas (if used).
Principle of Laser Welding Machine
Laser welding works on the principle of high-intensity light energy focused to a small spot. The beam causes metal to absorb the energy, raise its temperature rapidly, and melt. The fiber laser beam is particularly efficient, with low divergence and high beam quality. Asian Laser’s fiber laser welders deliver deep, firm welds, with less heat-affected zone and minimal deformation.
Welding Positions: What is 1G 2G 3G 4G 5G 6G welding?
These refer to standardized welding positions:
| Position | Description |
| 1G | Flat groove welding |
| 2G | Horizontal groove welding |
| 3G | Vertical groove welding |
| 4G | Overhead groove welding |
| 5G | Pipe welding, fixed-position (rolled) |
| 6G | Pipe welding at 45° incline (most difficult) |
These designations help welders assess skill, qualification, and quality control.
How Does a Laser Welding Machine Work (Specifically)
- Laser generation: A fiber laser source creates a beam, often via stimulated emission in doped fibre.
- Beam delivery: Through fiber optics or beam guidance, the laser is delivered precisely to the welding head.
- Focusing: The head has lens optics to focus the beam to a tiny spot.
- Pulse control: For pulsed lasers, each pulse’s energy, duration, and frequency are tuned. Asian Laser’s machines support precise pulse control to manage heat input and weld profile.
- Welding: The head is manipulated (manually or via CNC) over the joint, producing deep, controlled welds.
- Cooling & solidification: After welding, rapid cooling yields a narrow weld bead with minimal thermal distortion.
Electric vs Laser Welding: Which One to Use?
- Electric Welding: Generally lower cost, widely used, good for thick materials, but larger heat-affected zones and more distortion.
- Laser Welding: High precision, minimal HAZ, fast, deep welds, suited for delicate work (jewellery, electronics, moulds). Asian Laser specializes in laser welding machines for both jewellery (ALD/ALDC/ALDT series) and industrial applications (ALCC, ALS, ALDF, etc.)
Does Welding Machine Work on AC or DC?
- Electric welding machines: Can use AC or DC. TIG welding often uses DC (for stability), whereas some stick welders or older machines may use AC.
- Laser welding machines: Use electric power (AC from mains) to pump the laser source, but the welding itself is via light, not current.
Safe Work Procedure for Welding Machines
Safety is critical. Here are safe work procedures (especially for laser welding):
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Helmet (for arc), laser-safe goggles, gloves, apron.
- Ventilation: Ensure fumes, smoke are extracted.
- Beam control: Never look directly into a laser beam; ensure the beam path is enclosed.
- Training: Operators must be trained in parameter settings, alignment, and usage. At Asian Laser, training is provided at installation.
- Maintenance: Schedule preventive maintenance; Asian Laser provides 24×7 service and spare parts.
- Emergency procedures: Know how to shut down the machine, cover mirrors/lenses, and protect optics.
Welding Machine for Small Work: Repair & Precision
For small, high-precision welding tasks especially in jewellery applications, desktop laser welding machines are the most suitable. The Asian Laser’s ALD 200 is a jewellery-focused desktop laser welder designed for intricate repairs, micro-welding, and working on precious metals such as gold, silver, and platinum. Its stable chamber, controlled laser output, and minimal heat-affected zone make it ideal for detailed repair work where accuracy and metal integrity are essential.
4 Types of Welding Machines
Here are four common welding machine types:
- Fiber Laser Welding Machine
- Desktop Laser Welding Machine
- Hand-held Pen Laser Welder
- Industrial Laser Welding Machine
Why Choose Asian Laser
- Over 30 years of experience in laser technology
- ISO and CE certified company, providing installation, training, repair, and preventive maintenance.
- Supplier of a wide range of laser welding machines for jewellery, industrial mould repair, and more.
- 24×7 service, spare parts, strong customer support, reliable quality.
FAQs
-
How does a welding machine work step by step?
A welding machine works by preparation, setting parameters, generating energy (arc or laser), delivering that energy to the workpiece to form a molten pool, controlling the weld pool, allowing solidification, and then performing post-weld inspection and finishing.
-
What is the principle of an electric welding machine?
It uses an electric arc or resistance to generate heat, melting the metal via current, voltage and polarity control.
-
What is the principle of a laser welding machine?
A highly focused laser beam delivers energy to a tiny spot, melts the metal locally, forming a weld with minimal heat-affected zone.
-
What is 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, 6G welding?
The standard welding positions include flat (1G), horizontal (2G), vertical (3G), overhead (4G), fixed pipe (5G), and 45° inclined pipe (6G).
-
Does a welding machine work on AC or DC?
Electric welders can use AC or DC depending on the process. Laser welders use AC power to power the laser, but welding is via light.
-
What safety procedures should be followed when using a welding machine?
Use PPE, control ventilation, proper training, beam path safety (for lasers), regular maintenance, emergency shutdown protocols.
-
Which welding machine is good for small work or jewellery?
Pen-type laser welders (like ALLF 500) or desktop laser welders (ALDT) are ideal for precision and small-scale work.